
Brain tumor surgery is a medical procedure aimed at removing or reducing a brain tumor. The surgery typically involves a craniotomy, where a section of the skull is temporarily removed to access the tumor. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy brain tissue. The type of surgery depends on the tumor’s location, size, and type. Post-operative care is critical for recovery, and additional treatments like radiation or chemotherapy may be necessary.

Spinal decompression and fusion are surgical procedures used to treat spinal conditions like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease.
Spinal Decompression: This procedure involves removing parts of a disc, bone, or ligaments that are pressing on the spinal cord or nerves. It aims to relieve pain, numbness, and weakness caused by nerve compression.
Spinal Fusion: After decompression, spinal fusion is performed to stabilize the spine by fusing two or more vertebrae together using bone grafts, screws, or plates.
Together, these procedures help alleviate pain and improve spinal stability and function.

Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical treatment used to manage symptoms of neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. The procedure involves implanting a small device (similar to a pacemaker) in the brain, which sends electrical impulses to targeted areas of the brain. These impulses help regulate abnormal brain activity, improving movement control and reducing symptoms. DBS is typically used when medications are ineffective, and it can significantly enhance the quality of life for patients.

Stroke treatment and rehabilitation focus on minimizing brain damage and helping the patient regain lost functions. Immediate treatment involves medications to dissolve blood clots or surgical procedures to remove blockages or repair ruptured blood vessels. After the acute phase, rehabilitation begins to help the patient recover motor skills, speech, and cognitive abilities through physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. The goal is to improve independence and quality of life, with therapy tailored to the patient's specific needs and progress.

Epilepsy surgery is a treatment option for patients with epilepsy who do not respond well to medications. The procedure involves removing or altering the part of the brain responsible for causing seizures. Before surgery, a thorough evaluation is conducted, including brain imaging and monitoring, to identify the precise location of seizure activity. Common types of epilepsy surgery include lobectomy, lesionectomy, or the implantation of a device like a Vagus Nerve Stimulator (VNS). The goal is to reduce or eliminate seizures and improve quality of life.

Parkinson’s disease management involves medications like Levodopa to address motor symptoms, along with therapies for better quality of life. Physical therapy improves movement and balance, while speech therapy helps with communication and swallowing issues. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) may be considered for patients not responding to medication. Lifestyle changes, including regular exercise and a healthy diet, play a key role in managing symptoms. Ongoing support from healthcare professionals helps optimize treatment and maintain independence.

Disc replacement surgery is a procedure where a damaged spinal disc is replaced with an artificial one to relieve pain and improve mobility. It is often used to treat conditions like degenerative disc disease or herniated discs that don’t respond to conservative treatments. The surgery involves removing the damaged disc and inserting a prosthetic disc between the vertebrae. This helps restore normal spinal movement and stability while reducing pain. Recovery includes physical therapy and gradual return to normal activities.

Neuro-endoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to treat brain and spinal conditions. It involves inserting a small camera (endoscope) through tiny incisions to view and treat areas of the brain or spine. The procedure is often used for conditions like brain tumors, hydrocephalus (fluid buildup), and spinal cysts. Neuro-endoscopy reduces the need for larger incisions, leading to shorter recovery times, less pain, and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery.
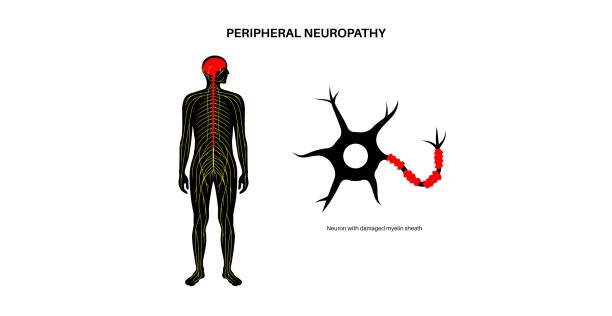
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and neuropathy management focus on symptom control, slowing disease progression, and improving quality of life.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Treatment includes disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) to slow progression, steroids for flare-ups, and medications for symptoms like spasticity, fatigue, and pain. Physical therapy and lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, help maintain function.
Neuropathy: Management focuses on controlling the underlying cause (e.g., diabetes) and relieving symptoms with pain relievers, anti-seizure drugs, and physical therapy to improve strength and mobility.