
Prenatal care refers to the healthcare provided during pregnancy, including regular check-ups, screenings, and advice to ensure both mother and baby's health. It involves monitoring fetal development, managing complications, and offering guidance on nutrition and lifestyle. Postnatal care focuses on the well-being of the mother and newborn after childbirth. It includes monitoring the mother's recovery, providing breastfeeding support, newborn care, and addressing physical or emotional concerns during the early weeks and months after delivery, ensuring the health and comfort of both.

Normal and cesarean delivery are two common methods of childbirth. Normal delivery involves the natural birth of a baby through the vaginal canal, usually with fewer complications and quicker recovery. It allows early mother-baby bonding and breastfeeding. Cesarean delivery, or C-section, is a surgical procedure in which the baby is delivered through incisions in the abdomen and uterus. It is performed when vaginal delivery is risky for the mother or baby. Recovery takes longer and requires proper medical care and rest.
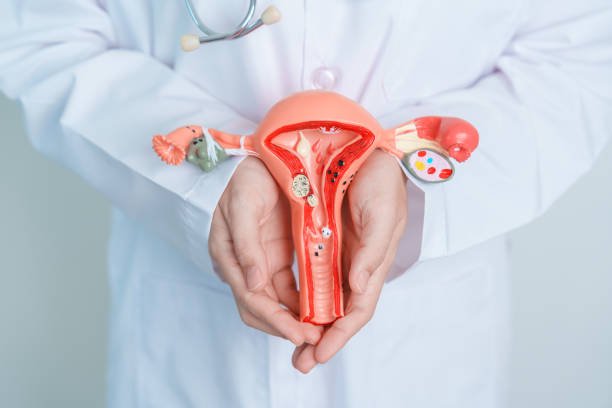
Hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman's uterus. It is commonly performed to treat conditions like uterine fibroids, heavy bleeding, endometriosis, or gynecologic cancers such as cervical, uterine, or ovarian cancer. Depending on the case, the surgery may also involve removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. After a hysterectomy, a woman can no longer become pregnant. Recovery time varies based on the type of surgery—abdominal, vaginal, or laparoscopic—and proper post-operative care is important for healing and well-being.
Laparoscopic gynecological surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the female reproductive system. It involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a camera and surgical instruments are inserted. Common uses include treatment of ovarian cysts, endometriosis, fibroids, ectopic pregnancy, and for performing hysterectomy. This technique offers several benefits such as less pain, smaller scars, shorter hospital stay, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery, making it a preferred option for many patients.

Treatment for PCOS and Endometriosis focuses on managing symptoms and improving overall health. For PCOS, lifestyle changes like healthy eating, weight management, and regular exercise are key. Medications such as birth control pills help regulate hormones, and metformin may improve insulin sensitivity. Endometriosis treatment includes pain relief through anti-inflammatory drugs, hormone therapy to reduce tissue growth, and sometimes laparoscopic surgery to remove affected areas. Both conditions require personalized treatment plans based on the patient’s symptoms, age, and fertility goals to ensure effective care.

Menopause management focuses on relieving symptoms and supporting overall health during the transition. Common symptoms include hot flashes, mood changes, sleep disturbances, and vaginal dryness. Treatment options vary based on individual needs and may include lifestyle changes, hormone replacement therapy (HRT), and non-hormonal medications. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques like yoga or meditation can also help. Regular health check-ups are important to monitor bone density and heart health, as hormonal changes during menopause can increase related risks.

Uterine fibroid removal is done to treat noncancerous growths in the uterus that may cause heavy bleeding, pain, or fertility issues. Treatment options include medication to shrink fibroids or surgical procedures like myomectomy, which removes fibroids while preserving the uterus, and hysterectomy, which removes the uterus completely. Minimally invasive methods such as laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery are often preferred for faster recovery. The choice of treatment depends on the size, location, symptoms, and the patient’s desire to maintain fertility.

Colposcopy and biopsy are diagnostic procedures used to examine and test the cervix for abnormalities, often following an abnormal Pap smear result. During a colposcopy, a doctor uses a special microscope to closely inspect the cervix, vagina, and vulva for any signs of disease. If abnormal areas are found, a biopsy is performed, where a small sample of tissue is removed for laboratory analysis. These procedures help diagnose conditions like cervical dysplasia or cancer, guiding further treatment if necessary.