
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a surgical procedure used to treat blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. It improves blood flow to the heart by using a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body to bypass the blocked artery, reducing chest pain and preventing heart attacks.

Angioplasty and Stent Placement is a procedure used to treat blocked or narrowed coronary arteries caused by plaque buildup. A catheter with a balloon at its tip is inserted into the artery and inflated to widen the blockage, improving blood flow. In many cases, a stent, which is a small mesh tube, is placed to keep the artery open. This procedure is minimally invasive, performed under local anesthesia, and offers quicker recovery compared to traditional surgery. It helps relieve symptoms like chest pain (angina) and reduces the risk of heart attacks. Angioplasty and stent placement are commonly recommended for patients with coronary artery disease.
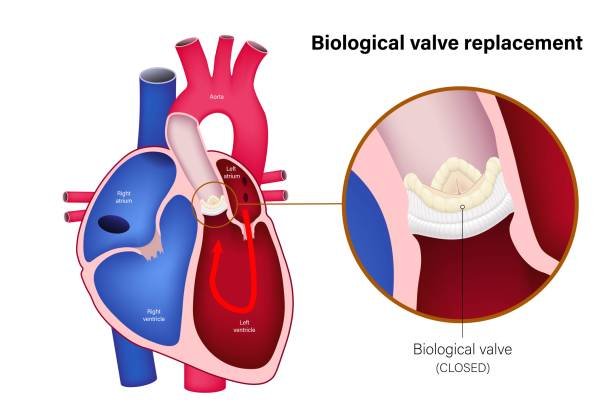
Heart Valve Replacement or Repair is a surgical procedure used to treat damaged or diseased heart valves. The heart has four valves that regulate blood flow, and if any valve becomes narrowed, leaky, or dysfunctional, it can impair the heart's ability to pump blood effectively. During valve repair, the surgeon may reshape or repair the damaged valve to restore normal function. In cases where repair is not possible, valve replacement is performed, where the damaged valve is replaced with either a mechanical valve or a biological valve (from animal tissue). This procedure helps improve heart function, relieves symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath, and reduces the risk of heart failure.

Pacemaker or ICD (Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator) implantation is a procedure to treat heart rhythm disorders. A pacemaker is a small device implanted under the skin to help regulate slow heartbeats by sending electrical signals to the heart. It ensures the heart maintains a normal rhythm. An ICD, on the other hand, is used for people at risk of life-threatening arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms), like ventricular fibrillation. The ICD monitors the heart's rhythm and can deliver a shock to restore a normal heartbeat if needed. Both devices are implanted via a minimally invasive procedure and help improve quality of life by preventing dangerous heart events and restoring normal heart function.

A heart transplant is a surgical procedure in which a diseased or failing heart is replaced with a healthy heart from a deceased donor. It is usually recommended for patients with end-stage heart failure or severe heart conditions that cannot be managed with medications or other surgeries. Before the transplant, patients undergo a thorough evaluation to ensure they are suitable candidates. Once a matching donor heart is found, the damaged heart is removed and replaced with the donor organ. The patient must take lifelong immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection. A successful heart transplant can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life, survival rate, and ability to perform everyday activities.

Atrial Fibrillation Surgery, often performed as the Maze Procedure, is used to treat atrial fibrillation (AFib), a common type of irregular heartbeat. In this surgery, the surgeon creates a series of precise scar lines in the upper chambers of the heart (atria) using a scalpel, heat, or cold energy. These scar lines disrupt the abnormal electrical signals that cause AFib, helping restore a normal heart rhythm. The Maze Procedure can be performed through traditional open-heart surgery or minimally invasive techniques, especially when combined with other cardiac surgeries. It is typically recommended when medications or catheter ablation have not been effective. This procedure can significantly reduce symptoms and lower the risk of stroke and heart failure.

Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery (MICS) refers to heart procedures performed through small incisions in the chest, without opening the breastbone. This technique is used for various surgeries such as valve repair or replacement, coronary artery bypass, and atrial septal defect repair. Special instruments and cameras are used to perform the surgery with precision. MICS offers several benefits over traditional open-heart surgery, including less pain, reduced blood loss, fewer complications, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery. Patients often experience smaller scars and return to normal activities sooner. This approach is ideal for those who qualify based on their heart condition and overall health.
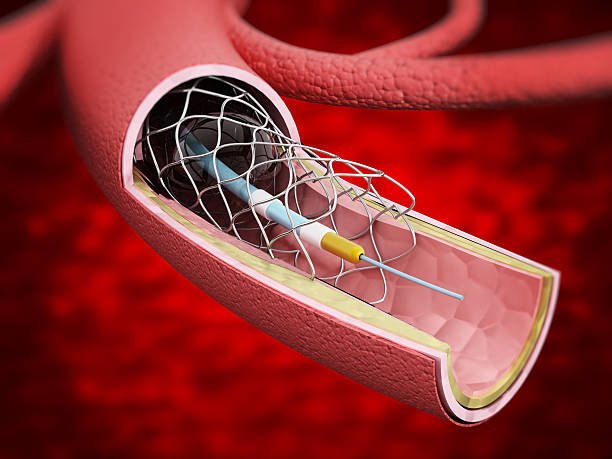
Cardiac Catheterization is a diagnostic and sometimes therapeutic procedure used to examine how well the heart is functioning. During the procedure, a thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, usually in the groin or arm, and guided to the heart. It allows doctors to check for blocked arteries, measure pressures in the heart chambers, and evaluate heart valve function. In some cases, treatments like angioplasty or stent placement can be done at the same time. It is minimally invasive and typically performed under local anesthesia. Cardiac catheterization provides crucial information for diagnosing heart conditions and planning appropriate treatments with minimal recovery time.

Echocardiogram and Stress Testing are non-invasive diagnostic tools used to evaluate heart health. An echocardiogram uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart, allowing doctors to assess heart structure, function, and blood flow. It helps detect conditions like valve problems, heart failure, and congenital defects. Stress testing, on the other hand, evaluates how the heart performs under physical exertion, usually using a treadmill or medication that simulates exercise. It helps identify issues like coronary artery disease and irregular heart rhythms that may not appear at rest. Together, these tests provide valuable insights into heart performance and guide decisions on treatment or further investigation.